The Power of Proof of Work: Understanding the Backbone of Cryptocurrency
Proof of work (PoW) is the backbone of many cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin and Ethereum. It’s a decentralized consensus mechanism that requires significant computing effort from a network of devices. But what exactly is proof of work, and how does it work?
A Brief History of Proof of Work
The concept of proof of work was first introduced by Hal Finney in 2004, and it was later adopted by Bitcoin in 2009. Since then, it has become a widely used consensus mechanism in the cryptocurrency space.
How Proof of Work Works
Proof of work is a competitive process that requires miners to expend computational effort to solve complex mathematical puzzles. The miner who solves the puzzle first gets to add a new block of transactions to the blockchain and is rewarded with newly minted cryptocurrency.
The process of proof of work can be broken down into several steps:
- Block Creation: Miners create a temporary file, known as a block, which contains a list of transactions.
- Hashing: Miners use a hashing algorithm to create a unique digital fingerprint, or hash, for each block.
- Proof of Work: Miners compete to find a hash that meets a certain criteria, such as having a certain number of leading zeros. This requires significant computational effort.
- Block Addition: The miner who finds a valid hash gets to add the block to the blockchain and is rewarded with cryptocurrency.
The Benefits of Proof of Work
Proof of work has several benefits, including:
- Security: Proof of work makes it extremely difficult for a single entity to control the network, as it would require significant computational power.
- Decentralization: Proof of work allows for decentralized transaction processing, without the need for a trusted third party.
- Incentivization: Proof of work incentivizes miners to participate in the network, as they are rewarded with cryptocurrency for their efforts.
The Drawbacks of Proof of Work
While proof of work has several benefits, it also has some drawbacks, including:
- Energy Consumption: Proof of work requires significant amounts of energy, which can be detrimental to the environment.
- Centralization: While proof of work is decentralized in theory, in practice, it has led to the centralization of mining power in the hands of a few large mining pools.
Proof of Work vs. Proof of Stake
Proof of work is not the only consensus mechanism used in cryptocurrency. Another popular mechanism is proof of stake (PoS), which uses a different approach to validate transactions.
In Conclusion
Proof of work is a complex and fascinating topic that is at the heart of many cryptocurrencies. While it has its drawbacks, it has also enabled the creation of decentralized, trustless systems that are revolutionizing the way we think about money and finance.
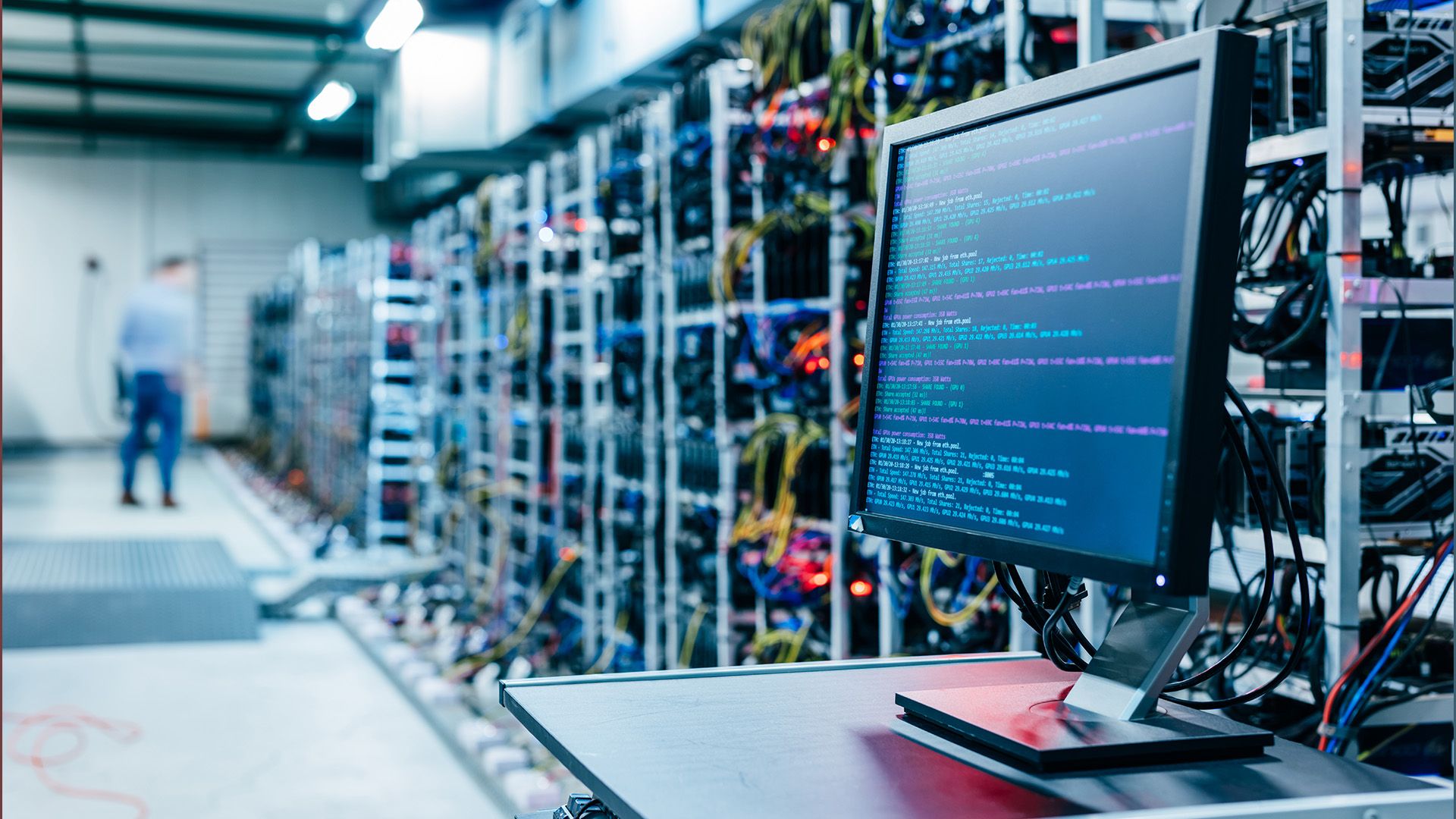
Bitcoin mining is a competitive process that requires significant computational effort.
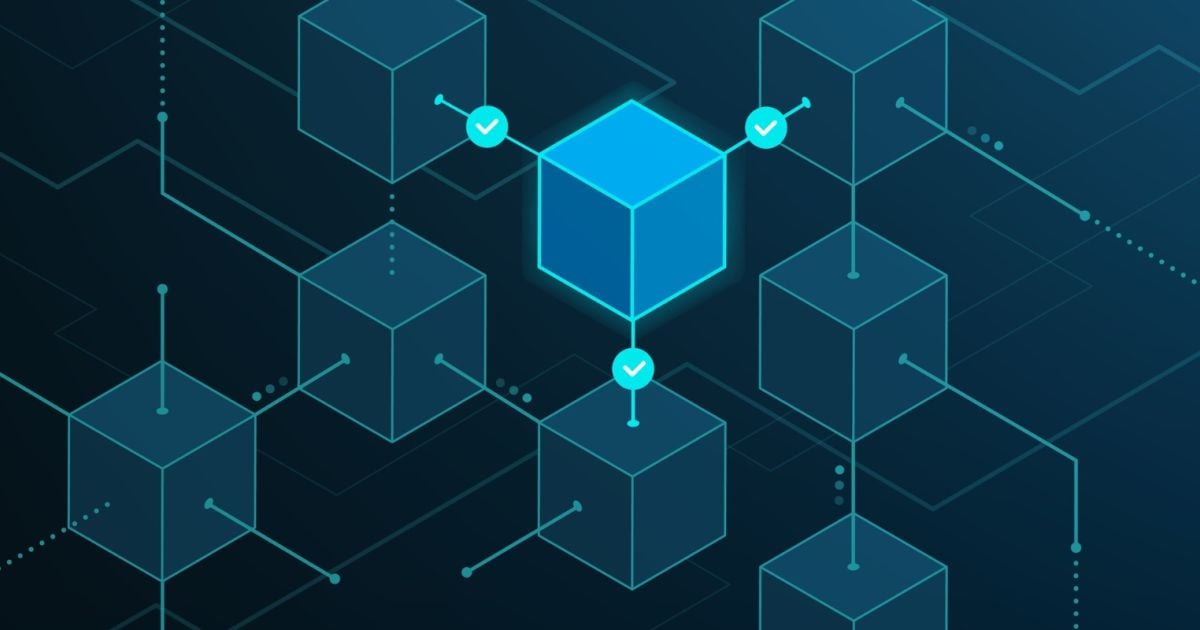 The blockchain is a decentralized ledger that records all transactions on the network.
The blockchain is a decentralized ledger that records all transactions on the network.