Cryptocurrency Myths Debunked
Many people are new to cryptocurrency, which is why there is a lot of mystery surrounding it — leading some people to believe in myths. That’s because sometimes people receive half-baked information that doesn’t tell the whole story.
 Cryptocurrency myths abound, but what’s the truth?
Cryptocurrency myths abound, but what’s the truth?
Here are the seven biggest myths about cryptocurrency, debunked.
Myth 1: Cryptocurrency is a currency of criminals and fraudsters
Cryptocurrency is based on new technology, and many people do not understand it. As a result, they may mistakenly believe that it is money used by criminals and fraudsters. But that is not true. Bitcoin is the most secure form of digital currency and was created to establish a decentralized digital currency free from the control of governments and central banks.
Bitcoin is the most secure form of digital currency.
Moreover, fraud, scams, ponzi schemes, money laundering, bribery, illicit financing, and corruption have been prevalent in every society for ages. Cash, which cannot be traced, remains the most popular method for illegal services and goods, not cryptocurrency.
Myth 2: Crypto is not safe and secure
Bitcoin was created to provide safe and secure access to money. Since crypto is created on a blockchain network, each transaction made can be verified and checked. People face problems when they don’t store their cryptocurrency on a reliable wallet and exchange. So, do your research before storing your money in a crypto wallet.
 Blockchain technology ensures secure transactions.
Blockchain technology ensures secure transactions.
Myth 3: Cryptocurrency is anonymous and can’t be traced
Many consider cryptocurrency anonymous and untraceable because Satoshi Nakamoto, a pseudonym used by the creator (or creators) of Bitcoin, is anonymous. But that’s not the case. Nakamoto’s anonymity helped maintain Bitcoin’s ethos as a decentralized, resistant-to-censorship currency.
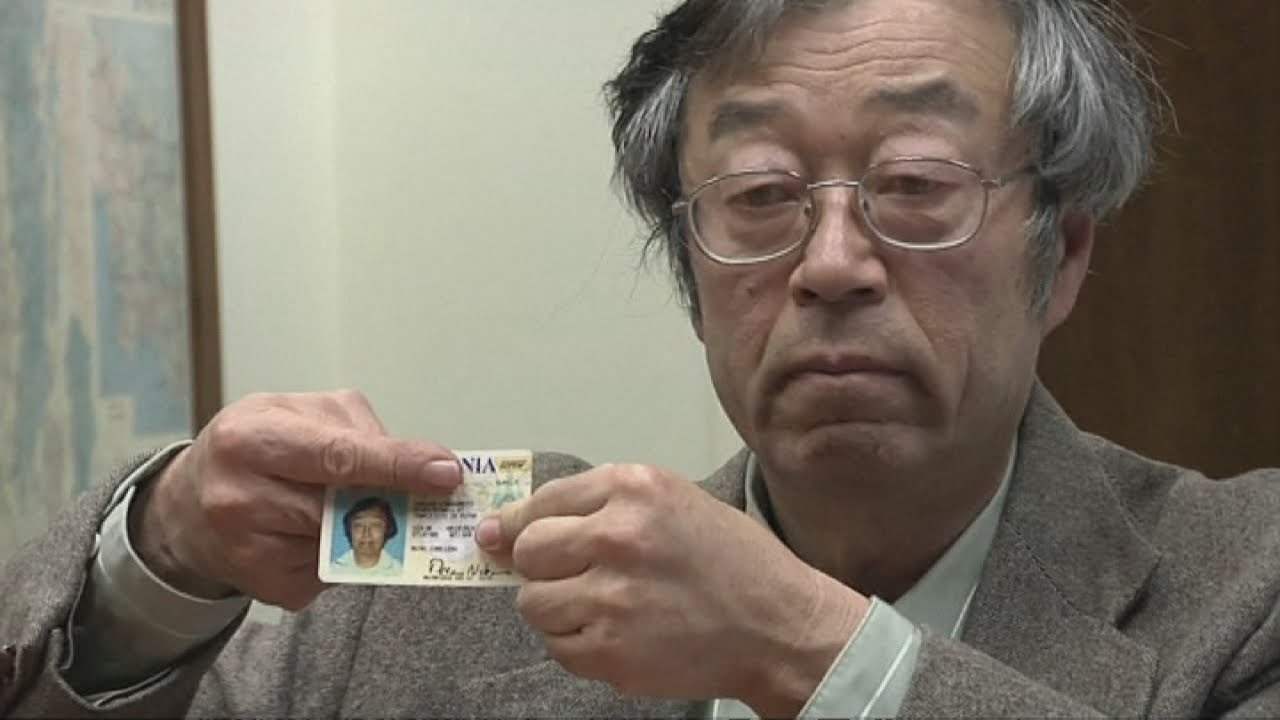 Satoshi Nakamoto’s anonymity helped maintain Bitcoin’s ethos.
Satoshi Nakamoto’s anonymity helped maintain Bitcoin’s ethos.
Cryptocurrency operates on a public blockchain, so anyone can trace its history of transactions. Cryptocurrency can be sent and received without revealing personally identifying information, but crypto addresses are forever retained on the blockchain.
Myth 4: Cryptocurrency is unregulated
While cryptocurrency has not yet undergone a robust regulatory process, that doesn’t mean there are no authorities to oversee it. Since 2013, cryptocurrency has been regulated under the Bank Secrecy Act in the U.S.
 Cryptocurrency regulation is evolving.
Cryptocurrency regulation is evolving.
The Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), which is part of the Treasury Department, collects and analyzes information about financial transactions related to cryptocurrencies. Similarly, cryptocurrencies are treated as capital gains or income depending on how and how long you hold them, and they are taxable in the U.S. The IRS considers crypto a digital asset and treats it like stocks, bonds, and other capital assets. Taxation laws also exist in Europe, the United Kingdom, India, and China.
Myth 5: Crypto has no real value
Many believe that crypto is a bubble that will burst soon and be worthless. The argument is bogus as Bitcoin emerged as a medium of exchange a long time ago and now many companies such as AT&T, AMC, X, and Tesla accept Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies as a mode of payment.
 Many companies accept Bitcoin as a mode of payment.
Many companies accept Bitcoin as a mode of payment.
Moreover, Bitcoin is also a form of asset, like stocks, that is traded between people. That’s why financial institutions such as BlackRock, Fidelity, and others have entered the crypto world, offering different types of crypto products.
Myth 6: Crypto will replace the U.S. dollar
A common misconception about Bitcoin is that it was created after the 2008 financial crisis and, therefore, poses a threat to the U.S. dollar. Firstly, Bitcoin was created simultaneously with the 2008 crisis, but there is no correlation between the two. Secondly, Bitcoin is only a decentralized digital form of currency.
 Bitcoin is not a replacement for the U.S. dollar.
Bitcoin is not a replacement for the U.S. dollar.
The development of fiat currencies including the U.S. dollar took a long time, and replacing them is not an easy task because banks monitor the economy through such currencies, and governments make policies accordingly.
Myth 7: Crypto is bad for the environment
It’s true that the mining of Bitcoin is an energy-intensive process that consumes as much energy as the entirety of Switzerland. However, not all cryptocurrencies require excessive electricity for transaction validation. Cryptocurrency and blockchain technology continue to evolve, with some taking steps to reduce their environmental impact.
 Sustainable mining practices are emerging.
Sustainable mining practices are emerging.
Moreover, the environmental impact depends greatly on the energy source used for mining operations and its impact on the power grid. Now, many mining companies are utilizing renewable energy, such as geothermal energy, to validate transactions, thus reducing the environmental impact.